|
TAO
2.1.1
|
All Classes Namespaces Files Functions Variables Typedefs Enumerations Enumerator Friends Macros Pages
|
TAO
2.1.1
|
A "Principal" identifies an authenticated entity in the network administration framework. More...
#include <Principal.h>
Public Types | |
| typedef Principal_ptr | _ptr_type |
| typedef Principal_var | _var_type |
Public Member Functions | |
| unsigned long | _incr_refcount (void) |
| unsigned long | _decr_refcount (void) |
| Principal (void) | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static Principal * | _duplicate (Principal *) |
| static Principal * | _nil (void) |
Public Attributes | |
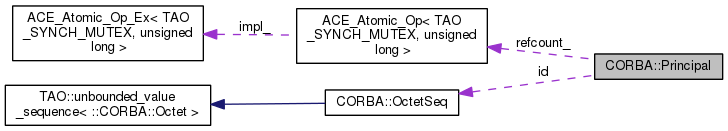
| CORBA::OctetSeq | id |
Protected Member Functions | |
| ~Principal (void) | |
| Destructor. | |
Private Member Functions | |
| Principal & | operator= (const CORBA::Principal_ptr &) |
| Principal (const CORBA::Principal_ptr &) | |
Private Attributes | |
| ACE_Atomic_Op< TAO_SYNCH_MUTEX, unsigned long > | refcount_ |
| Reference counter. | |
A "Principal" identifies an authenticated entity in the network administration framework.
Identities are used to control acccess (authorization) as well as in audit trails (accountability).
| CORBA::Principal::Principal | ( | void | ) |
|
protected |
Destructor.
Protected destructor to enforce proper memory management through the reference counting mechanism.
|
private |
| unsigned long CORBA::Principal::_decr_refcount | ( | void | ) |
|
static |
| unsigned long CORBA::Principal::_incr_refcount | ( | void | ) |
|
static |
|
private |
|
private |
Reference counter.
 1.8.0-20120409
1.8.0-20120409