CCMPerf: Model Integrated Test &
Benchmarking Suite
Point of Contact: Arvind S. Krishna
arvindk@dre.vanderbilt.edu
Institute of Software Integrated Systems (ISIS)
1.0 Motivation
The motivation for this project is to develop an
open-source benchmarking suite CCMPerf for CoSMIC that will provide the modeler
a way of generating test cases/benchmark experiments for the various use-case
scenarios. The suite can then be used to run the test cases and examine and
capture
performance or for Quality Assurance purposes. Another use case for this tool is
the generation of daily regression tests for the purpose of
Quality Assurance. The use of CCMPerf enables creation of experiments that
measure black box, e.g., latency, throughput metrics that can be used to
know the consequences of mixing and matching component assemblies on a target
environment. CCMPerf, can also be used to synthesize experiments on a per
component basis, the motivation being to generate unit and regression tests.
A model based approach to benchmarking allows the modeler to generate tests at
the push of button. Without modeling techniques, these
tedious and error-prone code would have to be written by hand. In a hand crafted
approach, changing the configuration would entail re-writing the benchmarking
code. In a model based solution, however, the only change will be in the model
and the necessary experimentation code will be automatically generated. A model
based solution also provides the right abstraction to visualize and analyze the
Experiment rather than looking at the source code. In the ensuing paragraphs we
describe the design of CCMPerf.
The experiments in CCMPerf can be divided into the
following two experimentation
categories:
- Distribution middleware tests that
quantify the performance of CCM-based applications using black box techniques
- Domain-specific middleware tests that
quantify the suitability of CCM implementations to meet the QoS requirements
of a
particular DRE application domain, such as static linking and deployment of
components in the Boeing Bold Stroke avionics mission
computing architecture.
2.0 CCMPerf Overview
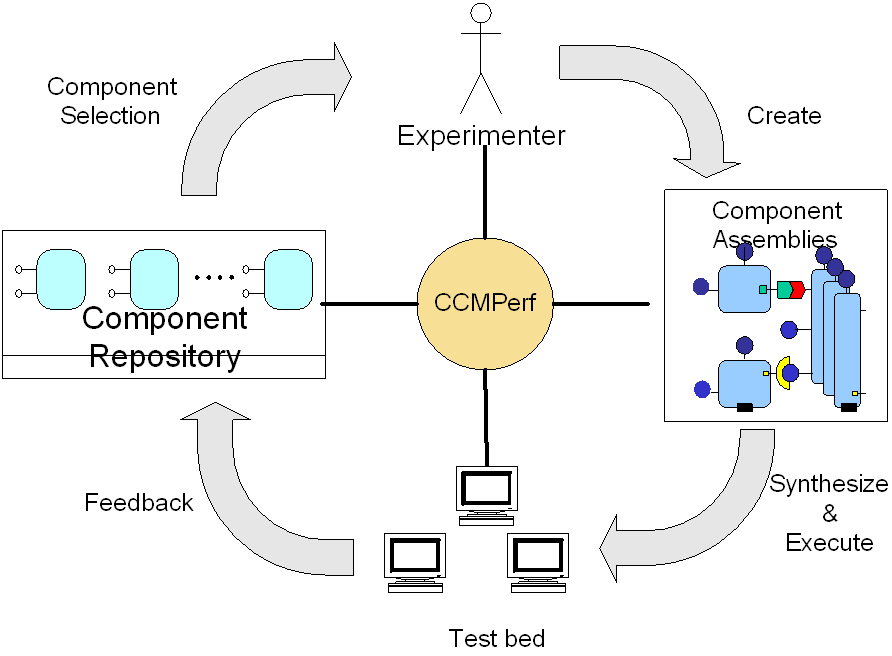
|
Figure on the right
illustrates the various stages involved in generating and running tests
using CCMPerf.
1: Using the component
repository, an experimenter selects the appropriate components that he wants
to experiment with
2: Using CCMPerf, he/she
models a component assembly.
3: CCMPerf the generates the
required descriptor files, benchmarking code and script files required to
perform the experiment.
4: The test is then run on a
target platform and the results generated are used as a "feed-back" to help
the planner make more informed decision |
 |
3.0 Meta-Model
The modeling paradigm of CCMPerf is defined in a manner
that will allow its integration with other paradigms, e.g., COMPASS and
Component Assembly
and Deployment Modeling Language (CADML). To achieve the aforementioned goal,
CCMPerf defines Aspects, i.e., visualization of the meta model
that allows the modeler to model component interconnection and metrics captured
through the above interaction. The following three aspects are defined in
CCMPerf
Configuration Aspect, that defines the interface
that are provided and required by the individual component,
Metric Aspect, that defines the metric captured
in the benchmark, and
Inter-connection Aspect, that defines how the
components will interact in the particular benchmarking experiment.
Additionally, a constraint checker validates the experiment precluding the
possibility of invalid configuration, such as:
- Conflicting metrics, e.g., using two different back
box metrics in a given experiment,
- Invalid connections, e.g., not connecting a required
interface with the corresponding provides interface and
- Incompatible exchange format, e.g., connecting a
point-to-point entity with a point to multi point entity.
Constraints are defined in the CCMPerf meta model are
defined using OCL. The use of constraints ensure that the experiment is correct
a priori
minimizing errors at run-time.
4.0 Interpretation Process
From the meta-model, an interpreter generates the
necessary files to configure the component assemblies and run the experiment.
This section
describes each of the files and their sample formats. In particular the
interpreter should generate the following files:
- Component-executor code, header and source
file for the executor logic that will be run as a part of the experiment,
- IDL code, this will be the IDL interface code
that will illustrate the contract, i.e., interface, exchanged between the
client and the server, and
- script files, these will be perl scripts that
will allow the experiment to be run on various platforms.
Additionally, the experiment, will require descriptor
files that provide meta-data to configure component servers and daemons
including:
- CORBA assembly descriptor (.cad), which is a
meta-information file with details of an assembly archive,
- CORBA component descriptor (.ccd), which is a
meta-information file that describes the features of a single component, and
- CORBA software descriptor (.csd), which is a
compressed file that contains one or more implementations of a component or an
interface.
5.0 Software Download and Documentation
The meta model for CCMPerf can be obtained from
www.dre.vanderbilt.edu/~arvindk/MIC
Arvind S. Krishna, Jaiganesh Balasubramanian, Aniruddha Gokhale,
Douglas C. Schmidt, Diego Sevilla, Gautam Thaker,
Empirically
Evaluating CORBA Component Model Implementations, Proceedings of the ACM
OOPSLA 2003 Workshop on Middleware Benchmarking, Anaheim, CA, October 26, 2003.
Send comments to: Arvind S. Krishna <arvindk@dre.vanderbilt.edu>
Last Updated:
11/18/2003
